Virginia Fake ID
Introduction
In today's digital age, the demand for fake IDs, particularly for states like Virginia, has surged. Whether it's for underage access to bars, clubs, or simply for privacy concerns, the need for high-quality, undetectable fake IDs is prevalent. Virginia, with its specific design features, security enhancements, and stringent regulations, has become a popular state of choice for fake ID producers and users alike. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the specifics of Virginia fake IDs, providing a thorough analysis of the product features, market demand, target audience, and essential considerations for those looking to purchase or sell these IDs.
Chapter 1: Understanding the Virginia Fake ID
1.1 What is a Virginia Fake ID?
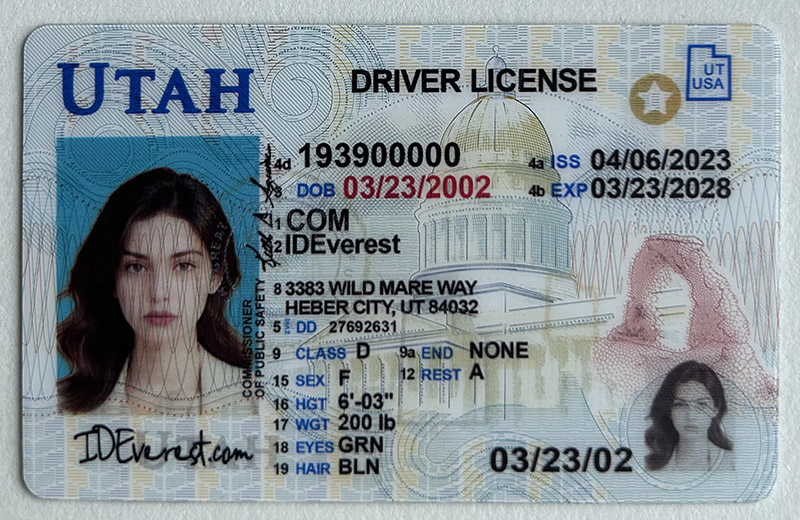
A Virginia fake ID is a counterfeit version of the official state identification card or driver's license, meticulously replicated to match the real Virginia ID's appearance, design, and security features. This includes details like holograms, UV markings, and unique fonts that align with Virginia's official license standards.
1.2 The Design and Features of a Virginia Fake ID
Virginia's official IDs have distinct design elements that make them challenging to replicate accurately. Here’s a breakdown of the key features:
- Holographic Overlay: Virginia IDs contain a hologram that reflects light at different angles, with visible text like "Virginia" or the state's emblem.
- Laser Engraved Features: The photo and some personal details on Virginia IDs are laser engraved, adding a raised texture to certain areas.
- UV Light Security Elements: Under UV light, additional markings become visible on the authentic ID, such as the state's seal or certain patterns.
- Microprinting and Ghost Images: Tiny text (microprinting) and faded images (ghost images) are embedded into the card to add an extra layer of security.
- Barcodes and Magnetic Strips: Scannable data strips contain information about the cardholder, and they must be programmed correctly for the ID to pass through scanning machines.
1.3 Authenticity vs. Fake: What Sets a Premium Virginia Fake ID Apart?
The difference between a subpar fake ID and a high-quality one lies in the attention to detail. Fake IDs that pass basic security checks (such as visual and tactile inspections) often fail when scanned or examined under UV light. High-quality Virginia fake IDs, on the other hand, integrate all the elements mentioned above with precision to closely mimic the real thing. The better the quality, the higher the chances it can bypass bouncers, scanners, and law enforcement scrutiny.
Chapter 2: Market Analysis for Virginia Fake IDs
2.1 The Demand for Fake IDs in the U.S.
In the United States, fake IDs have consistently been in demand, particularly among the youth demographic. Underage individuals often seek to obtain these IDs for various purposes, most commonly for gaining access to clubs, bars, and purchasing alcohol.
Virginia fake IDs, in particular, have seen a rise in demand due to the state’s relatively strict age verification policies at various establishments. Virginia is a hub for universities and colleges, further amplifying the demand for high-quality fake IDs among the student population.
2.2 Market Competitiveness and Leading Producers
With the increasing demand, numerous companies and online platforms have emerged, offering counterfeit Virginia IDs. However, not all providers are equal in terms of quality, security, and reliability. The market can be broadly divided into:
- Low-Cost Producers: Typically based overseas, these providers offer cheap, basic fake IDs that can often be spotted by trained personnel or modern scanning technology.
- Premium Producers: These are companies specializing in high-quality IDs that closely mimic all aspects of the original, including barcode functionality, UV markings, and detailed holograms. They charge higher prices but offer a product that is much more likely to evade detection.
Premium Virginia fake IDs command a higher price due to the complexity of replicating state-specific security features. Sellers focusing on quality over quantity tend to dominate this segment, catering to buyers willing to pay for authenticity.
2.3 Pricing Trends and Profit Margins
The price of a Virginia fake ID can vary depending on the quality, source, and additional features. Entry-level fake IDs may cost as little as $50, but they often lack the necessary details to pass a thorough inspection. Premium fake IDs, on the other hand, range between $100 to $200 per card, especially if they include scannable barcodes and authentic-feeling materials.
The profitability for producers is high, especially given the relatively low cost of materials and labor required to produce counterfeit IDs. However, producers also face risks of legal action and enforcement crackdowns, which can affect their operations.
Chapter 3: Product Features of a Virginia Fake ID
3.1 Essential Features of a High-Quality Virginia Fake ID
When evaluating a Virginia fake ID, there are several critical features that buyers should consider:
- Material Quality: The feel of the ID should be close to the official polycarbonate or PVC material used by the state.
- Accurate Replication of Security Features: Holograms, UV markings, and raised text must be replicated with high precision.
- Scannable Barcodes: The barcodes should contain accurate data corresponding to the ID information, ensuring that the card can pass electronic verification.
- Durability: The ID must withstand wear and tear, as official cards are built to last for several years.
- Photo Quality: The image on the ID should match the resolution and clarity of government-issued IDs, with no pixelation or blurriness.
3.2 Advanced Features: Going Beyond Basic Requirements
Some premium fake IDs offer additional features to increase the chances of passing both human and machine inspections:
- Custom Fonts and Textures: Advanced IDs replicate the specific fonts used in Virginia IDs, ensuring that even under close scrutiny, the text matches the original.
- Laser Engraving Technology: Top-tier producers use laser engraving to replicate the raised text on official IDs, providing an extra layer of authenticity.
- State-Specific UV Markings: Producers who invest in UV printing technology can mimic the hidden details that are only visible under blacklight, such as state seals or emblems.
3.3 Quality Assurance: How to Evaluate and Test Your Fake ID
After receiving a Virginia fake ID, there are several ways to evaluate its quality:
- Visual Inspection: Compare the card side-by-side with an authentic Virginia ID (if available), paying close attention to fonts, colors, and holographic elements.
- UV Light Test: Use a UV light to verify that hidden features like the state seal or security patterns are present.
- Scanning: Try scanning the barcode at a self-checkout or in-store age verification system to ensure it reads correctly.
- Weight and Thickness: Genuine IDs have a specific weight and thickness; a fake ID should feel comparable in your hand.
Chapter 4: Target Audience for Virginia Fake IDs
4.1 Primary Audience: College Students and Young Adults
The largest demographic purchasing fake IDs in the U.S. consists of young adults, primarily those under 21 who want to access age-restricted venues like bars and nightclubs. Virginia, in particular, is home to several large universities, including the University of Virginia and Virginia Tech, which foster environments where students seek fake IDs to circumvent age restrictions.
4.2 Secondary Audience: Individuals Seeking Privacy
A smaller but notable segment of the market includes individuals who seek fake IDs for privacy reasons. Some may wish to protect their personal information or engage in activities anonymously without being tracked by their real ID.
4.3 Geographical Demand Trends
Certain regions within Virginia, especially college towns like Charlottesville (University of Virginia) and Blacksburg (Virginia Tech), have a higher demand for fake IDs. Outside of Virginia, fake IDs from the state are also popular in areas like Washington D.C., Maryland, and other nearby states due to the ease of crossing state borders with a seemingly valid Virginia ID.
Chapter 5: Legal Implications and Risks
5.1 Legal Consequences of Owning a Fake ID
While the allure of owning a fake ID can be strong, it is crucial to understand the potential legal ramifications. In Virginia, possessing or using a fake ID is considered a criminal offense. Penalties can range from fines and community service to potential jail time and a permanent mark on one's criminal record.
5.2 Risks for Producers and Distributors
Fake ID producers and sellers also face significant legal risks, including federal charges for counterfeiting government-issued identification. Law enforcement agencies, including the FBI and Homeland Security, actively pursue operations selling counterfeit IDs, especially those involved in large-scale distribution.
5.3 How Buyers and Sellers Can Minimize Risks
Both buyers and sellers of Virginia fake IDs can take steps to minimize legal risks:
- Encryption and Secure Communication: Using secure, encrypted platforms like Telegram or Signal can reduce the risk of interception by law enforcement.
- Anonymity for Buyers: Using cryptocurrency like Bitcoin for purchases can help maintain anonymity.
- Discreet Shipping: Sellers often use discreet packaging and drop shipping techniques to avoid detection by postal authorities.
Chapter 6: Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Virginia fake IDs are among the most sought-after counterfeit identification products in the U.S., particularly among young adults and those living near border regions. With advancements in printing technology, modern fake IDs can replicate the state's design with impressive accuracy, including scannable barcodes and detailed holographic features.
However, potential buyers and sellers must weigh the risks carefully. While these products can provide temporary benefits, the legal consequences of being caught with or producing a fake ID are severe. For those seeking to enter the fake ID market, focusing on high-quality production and staying informed about state-specific security measures is crucial to avoiding detection.
Ultimately, the Virginia fake ID market, like all counterfeit identification markets, requires careful navigation to balance demand, profitability, and legal responsibility.
 A Night to Remember: Adventure
A Night to Remember: Adventure
 Title: Security Features of Ut
Title: Security Features of Ut
 Title: Texas Driver License Se
Title: Texas Driver License Se
 Fake Driver’s License Kansas
Fake Driver’s License Kansas